Definition Of Chicken Pox
Smallpox, medically called varicella, commonly suffered by children under the age of 10 years and more rarely affects adults. Almost all adults who have ever suffered from chicken pox will not be infected again.
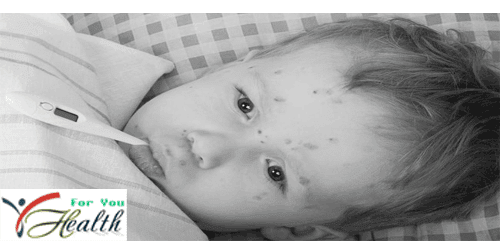 Disease caused by the varicella zoster virus is generally characterized by the appearance of a skin rash that becomes the main symptoms of chicken pox. The rash will turn into fluid-filled red bumps that itch which then will dry up, become raw, and chipped within 7-14 days. The parts of the body usually covered with chicken pox rash is the face, behind the ears, scalp, arms and legs.
Disease caused by the varicella zoster virus is generally characterized by the appearance of a skin rash that becomes the main symptoms of chicken pox. The rash will turn into fluid-filled red bumps that itch which then will dry up, become raw, and chipped within 7-14 days. The parts of the body usually covered with chicken pox rash is the face, behind the ears, scalp, arms and legs.
Treatment and Complications of Chickenpox
Chicken pox has no special handling steps. The aim of treatment is to reduce symptoms. Two types of drugs commonly used to treat smallpox is paracetamol to reduce fever and calamine lotion or powder to reduce the itching of the skin.
Not all children are infected with chickenpox can heal on its own without medical treatment. Unusual symptoms that you should be aware of is an infection that occurs in the skin rash or if your child has chest pain and difficulty breathing. Contact your doctor immediately if your child chickenpox condition more serious.
Conditions of adult chickenpox sufferers tend to be more severe and the risk of complications . Antidote to the virus (anti-virus) may be effective for treating adult patients with chickenpox if given early in the disease.
Chickenpox in pregnant women, newborns, and people with weakened immune systems are also more susceptible to serious complications. They should seek medical help immediately if exposed to the virus or experiencing symptoms .
Step Prevention Chickenpox
Chicken pox can be prevented by vaccination. In Indonesia alone, chicken pox does not include a list of immunizations required for children, but still recommended.
Transmission of measles are also generally very easy and fast to happen. Step prevention first deployment that can be done is to isolate people with chicken pox from public places such as schools or offices until the pimple dry out and become scabs.
The chickenpox virus most easily transmitted to 1-2 days before the rash appears until next week, when the rash has dried and become scabs.

Treatment and Complications of Chickenpox
Chicken pox has no special handling steps. The aim of treatment is to reduce symptoms. Two types of drugs commonly used to treat smallpox is paracetamol to reduce fever and calamine lotion or powder to reduce the itching of the skin.
Not all children are infected with chickenpox can heal on its own without medical treatment. Unusual symptoms that you should be aware of is an infection that occurs in the skin rash or if your child has chest pain and difficulty breathing. Contact your doctor immediately if your child chickenpox condition more serious.
Conditions of adult chickenpox sufferers tend to be more severe and the risk of complications . Antidote to the virus (anti-virus) may be effective for treating adult patients with chickenpox if given early in the disease.
Chickenpox in pregnant women, newborns, and people with weakened immune systems are also more susceptible to serious complications. They should seek medical help immediately if exposed to the virus or experiencing symptoms .
Step Prevention Chickenpox
Chicken pox can be prevented by vaccination. In Indonesia alone, chicken pox does not include a list of immunizations required for children, but still recommended.
Transmission of measles are also generally very easy and fast to happen. Step prevention first deployment that can be done is to isolate people with chicken pox from public places such as schools or offices until the pimple dry out and become scabs.
The chickenpox virus most easily transmitted to 1-2 days before the rash appears until next week, when the rash has dried and become scabs.


